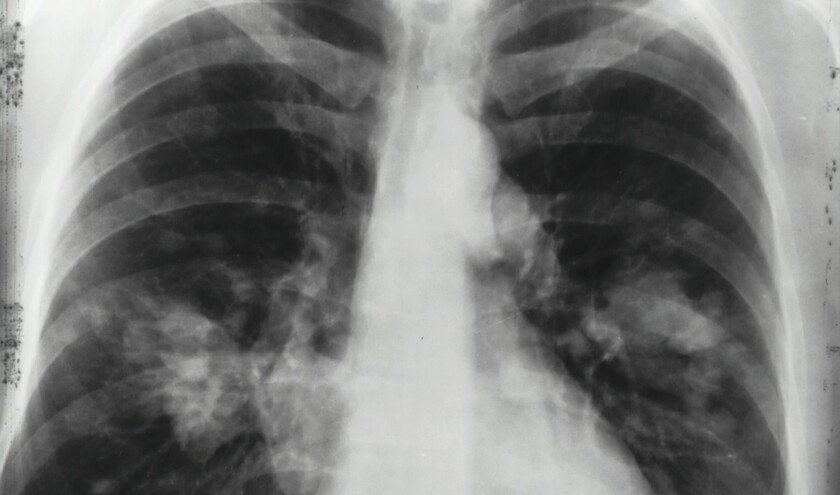
The University of St Andrews School of Medicine study, conducted with 12,000 smokers and ex-smokers, demonstrates how biomarkers - measurable indicators of biological changes - can identify individuals at high risk of lung cancer, leading to earlier detection and significantly improved outcomes.
The study, published in PLoS ONE, found that testing high-risk individuals with biomarkers led to a 40% reduction in deaths from lung cancer and other causes over five years.
The research team aims to explore how biomarker testing could enhance lung cancer screening programs currently being developed or implemented in several countries. This targeted strategy could improve the identification of individuals most at risk, ensuring that screening resources are used efficiently and effectively.
Dr Frank Sullivan, professor of primary care medicine at the University of St Andrews School of Medicine, said: ‘This study, along with others using imaging techniques, shows that earlier diagnosis of lung cancer is now possible. That is good news because, if caught early enough, the improved treatments now available have a much higher chance of success.'