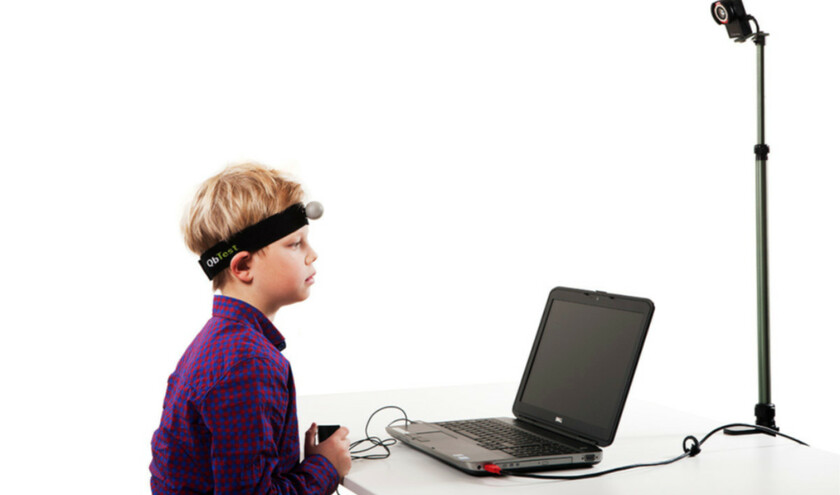
The NHS is now using a digital test to speed up the diagnosis of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children after successful trials by the NIHR.
QbTest is a computer-based test which measures attention, impulsivity, and activity. Over 20 minutes the child responds to target stimuli while ignoring other stimuli. A camera tracks the movements of a marker attached to the patient's head. The results are then compared to a group of children of the same age and gender who do not have ADHD. The results help clinicians reach a diagnosis.
The first independent randomised controlled trial AQUA Trial: Assessing QbTest Utility in ADHD found that the QbTest shortens the assessment cycle, doubles the likelihood of excluding ADHD in the first six months, and helped 85% of patients surveyed to better understand their symptoms.
Professor Richard Morriss, NIHR ARC East Midlands mental health and well-being theme lead, said: ‘There has been a fourfold increase in referrals for ADHD since the Covid-19 pandemic and this device can reduce time to an accurate diagnosis in children and young people by one third in terms of clinic time.
'NIHR ARC East Midlands worked with industry to help with this challenge. NICE has now recommended QbTest, which is now used in 70% of NHS services for ADHD in children and young people. NIHR ARC East Midlands is currently exploring how QbTest might also help with treating as well as diagnosing ADHD.'